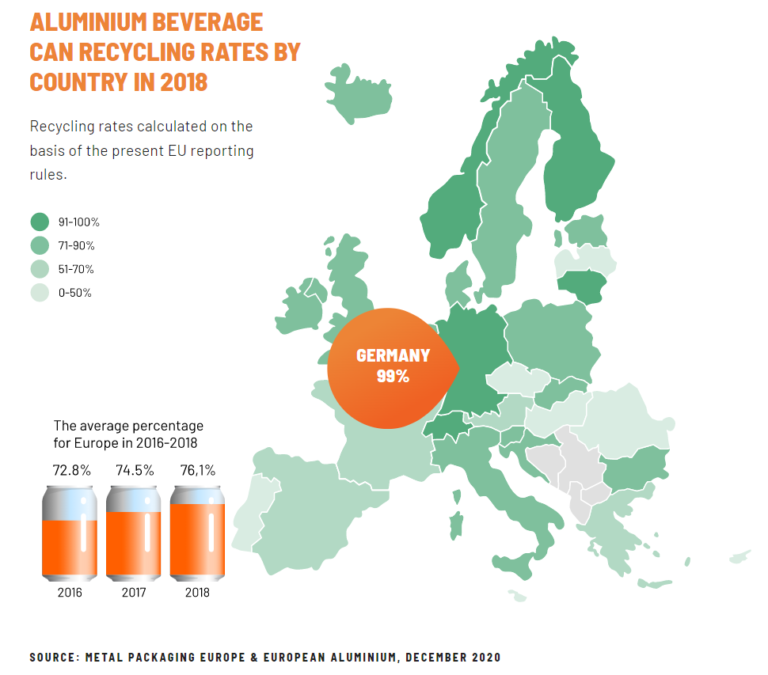
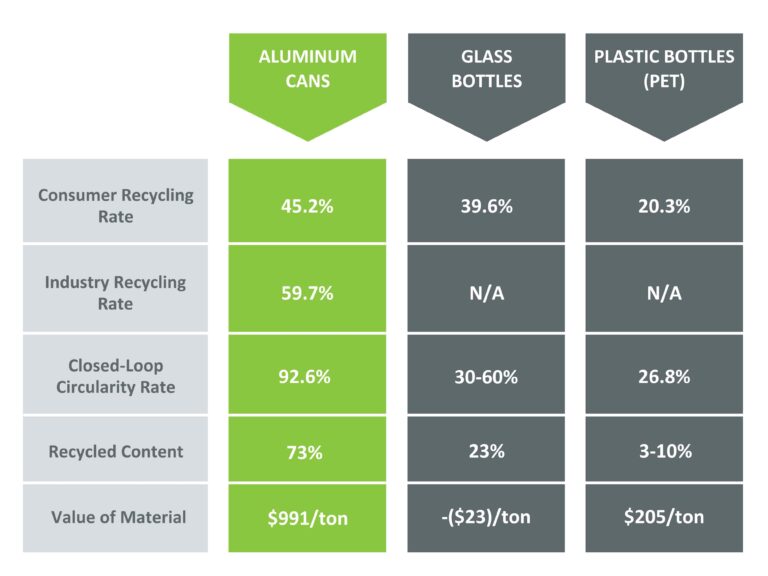
Responsibilities that go beyond just a “producers”
Campaigning for consumers to use cloth bags and reduce the use of plastic packaging might not be enough. Manufacturers, who play a significant role in creating waste and pollution, must also take responsibility.